Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) considerations have progressively permeated the corporate world. The Environmental, Social, and Sustainability Reporting (ESRS) is a new set of standards that requires organisations to disclose their impacts, risks and opportunities related to ESG topics.. The future of ESRS reporting promises to be transformative, driven by technological advancements, regulatory changes, and evolving stakeholder expectations.
Definition and Purpose of ESRS Reporting
The ESRS standards requires that companies document their environmental, social, and governance practices. The root of ESRS reporting is the early corporate social responsibility (CSR) movements of the 20th century. Initially voluntary, these disclosures evolved into structured reports as awareness of environmental and social issues grew.
Over the decades, frameworks like the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) and the Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB) emerged, setting the stage for today's sophisticated ESRS practices.The ESRS builds on these earlier frameworks and requires companies to integrate sustainability information into their management reports, ensuring that ESG considerations are a core part of corporate reporting.
Phasing in Period of ESRS Reporting
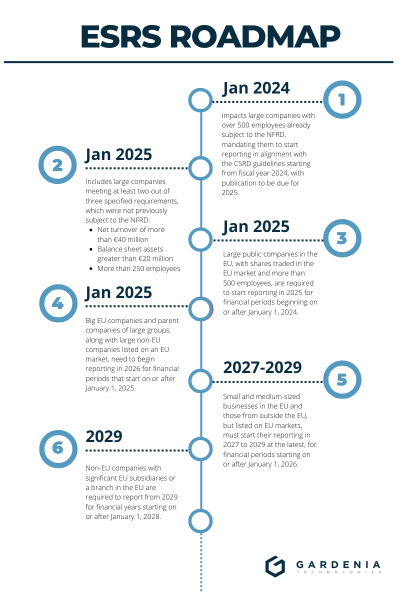
The European Sustainability Reporting Standards (ESRS) are set to be implemented in a phased approach, reflecting the diverse capacities and readiness levels of different companies. The initial phase, beginning in 2024, mandates that large public interest entities with over 500 employees start reporting. By 2025, the scope expands to include all large companies, defined as those meeting at least two of the following criteria: more than 250 employees, net turnover exceeding €40 million, or total assets above €20 million. Finally, from 2026, the ESRS requirements will apply to listed SMEs (excluding micro-enterprises), allowing these smaller entities additional time to prepare for comprehensive sustainability reporting. This staggered timeline ensures that companies of varying sizes and complexities can adapt to the new standards without overwhelming disruption.
Extension of the Value Chain Approach
The extension of the value chain approach within ESRS reporting is anticipated to significantly enhance the comprehensiveness and transparency of sustainability disclosures. Initially, companies are required to report on their direct operations, but from 2026 onwards, the obligation will extend to include the entire value chain. This means that businesses must account for the environmental, social, and governance impacts of their suppliers, distributors, and even end-users.
By incorporating value chain considerations, ESRS aims to provide a more holistic view of a company's sustainability performance, ensuring that indirect impacts are also addressed. This forward-thinking approach encourages companies to foster sustainable practices across their entire network, driving systemic change and promoting broader corporate accountability.
The Need for Enhanced ESRS Reporting
Growing Environmental and Social Concerns
The urgency of addressing climate change, biodiversity loss, and social inequities has never been greater. Enhanced ESRS reporting is essential in driving corporate accountability and ensuring that businesses contribute positively to these pressing global challenges.
Increasing Regulatory Requirements
Regulatory landscapes are tightening globally, with governments mandating more detailed and frequent ESRS disclosures. This shift towards stricter regulations underscores the need for companies to refine their reporting processes and ensure compliance.
Technological Advancements in ESRS Reporting
Role of Big Data and Analytics
Big data and advanced analytics are revolutionising ESRS reporting. These technologies enable companies to gather vast amounts of information, analyse trends, and make data-driven decisions. The ability to process and interpret large datasets enhances the accuracy and comprehensiveness of sustainability reports.
Using AI in ESRS Reporting
Artificial intelligence (AI) offers unprecedented opportunities for automating ESRS reporting processes. From real-time data collection to predictive analytics, AI facilitates more efficient and insightful reporting, helping companies stay ahead of regulatory and stakeholder demands.
Blockchain and its Impact on Transparency
Blockchain technology, known for its immutable and transparent nature, is poised to transform ESRS reporting. By ensuring data integrity and traceability, blockchain can enhance trust and accountability in sustainability disclosures.
Standardisation and Harmonisation of ESRS Reporting
International Standards and Frameworks
Global standards such as the GRI, SASB, and the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) provide comprehensive frameworks for ESRS reporting. These standards help ensure consistency, comparability, and reliability of sustainability information across organizations and regions.
Efforts Towards Global Harmonisation
Efforts are underway to harmonise ESRS reporting standards globally. Initiatives like the International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) Foundation's Sustainability Standards Board aim to create unified guidelines, reducing fragmentation and enhancing the clarity of sustainability disclosures. The ESRS standardises ESG regulation across Europe, and the gradual roll-out of the legislation means that all companies (excluding micro-entrepreneurs) will have to report eventually.
The Role of Government and Policy in Shaping the Future
Regulatory Trends and Future Policies
Governments worldwide are enacting stringent regulations to bolster ESRS reporting. Future policies are likely to emphasize comprehensive climate-related disclosures, human rights impacts, and biodiversity conservation, pushing companies towards more robust reporting practices.
Government initiatives and support programs play a vital role in promoting ESRS reporting. Grants, tax incentives, and public-private partnerships can help companies invest in the necessary technologies and frameworks to enhance their sustainability disclosures.
Corporate Responsibility and ESRS Reporting
Corporate buy-in is essential for effective ESRS reporting. Leadership commitment drives the integration of sustainability into business strategies, ensuring that ESRS practices are not merely compliance exercises but fundamental components of corporate identity.
Case Studies of Successful Corporate ESRS Reporting
Numerous companies have set benchmarks in ESRS reporting. BASF, a leading chemical company in Europe, has been actively preparing for ESRS implementation with CDP. They began with a gap analysis in December 2022, followed by topic-specific workshops and the appointment of "topic leads" responsible for coordinating compliance with ESRS standards. BASF has also engaged in monthly meetings to address emerging questions and align with auditors on the new requirements. Their approach emphasizes the importance of standardized sustainability reporting to provide stakeholders with meaningful and decision-relevant.
ESRS Reporting in Different Industries
The concept of materiality in European Sustainability Reporting Standards (ESRS) requires companies to focus on sustainability issues that are most relevant to their specific sector.
This sector-specific approach is driven by the unique operational impacts and stakeholder concerns associated with each industry.
- Energy and Natural Resources
- The energy and natural resources sector faces intense scrutiny due to its significant environmental impact. ESRS reporting in this industry focuses on emissions reduction, resource management, and community engagement, aiming to mitigate adverse effects and promote sustainable practices.
- Manufacturing and Heavy Industries
- Manufacturing and heavy industries are integral to global economies but pose substantial sustainability challenges. ESRS reporting in these sectors addresses issues like waste management, energy efficiency, and worker safety, driving improvements in both environmental and social performance.
- Technology and Telecommunications
- The technology and telecommunications sector, while less resource-intensive, has its own sustainability concerns, including electronic waste and data privacy. ESRS reporting helps these companies navigate these challenges, promoting transparency and responsible innovation.
- Financial Services
- The financial services industry plays a crucial role in funding sustainable development. ESRS reporting in this sector focuses on responsible investment practices, risk management, and the promotion of ESG principles in lending and investment decisions.
Future Trends in ESRS Reporting
Predictive Analytics and Proactive Reporting
Predictive analytics will become a cornerstone of future ESRS reporting, allowing companies to anticipate sustainability trends and proactively address potential issues. This forward-looking approach enhances strategic planning and risk management.
Real-Time Reporting Capabilities
Real-time reporting capabilities, enabled by advanced technologies, will provide stakeholders with up-to-date information on corporate sustainability performance. This immediacy fosters greater transparency and responsiveness to emerging issues.
Integration with Corporate Strategy and Decision-Making
The integration of ESRS reporting with corporate strategy and decision-making processes will ensure that sustainability considerations are embedded in all aspects of business operations. This holistic approach drives long-term value creation and resilience.
Challenges and Barriers to Future ESRS Reporting
Data Collection and Quality Issues
Data collection and quality remain significant challenges in ESRS reporting. Ensuring accurate, reliable, and comprehensive data is essential for credible sustainability disclosures, necessitating continuous improvements in data management practices.
Balancing Transparency with Competitive Advantage
Companies must balance the need for transparency with the protection of competitive advantage. Strategic disclosures can build trust without compromising proprietary information, striking a balance that benefits both stakeholders and the business.
Opportunities in the Future of ESRS Reporting
Enhancing Corporate Reputation and Brand Value
Robust ESRS reporting enhances corporate reputation and brand value. Transparent disclosures demonstrate a company's commitment to sustainability, attracting socially conscious consumers and investors.
Driving Sustainable Business Practices
ESRS reporting drives sustainable business practices by highlighting areas for improvement and promoting accountability. This iterative process fosters continuous enhancement of environmental and social performance.
Unlocking New Business Opportunities
Embracing ESRS reporting can unlock new business opportunities. Companies that lead in sustainability can differentiate themselves in the market, attract investment, and access new revenue streams through innovative, eco-friendly products and services.
Best Practices for Future-Proofing ESRS Reporting
Leveraging Advanced Technologies
Leveraging advanced technologies, such as AI, big data, and blockchain, is essential for future-proofing ESRS reporting. These tools enhance data accuracy, streamline processes, and provide deeper insights into sustainability performance.
Building Robust Reporting Frameworks
Building robust reporting frameworks ensures consistency, reliability, and comparability of ESRS disclosures. Adopting established standards and continuously refining reporting practices are key to achieving high-quality sustainability reports.
Continuous Learning and Adaptation
Continuous learning and adaptation are crucial for staying ahead in the evolving landscape of ESRS reporting. Companies must stay informed about regulatory changes, technological advancements, and emerging best practices to maintain the relevance and effectiveness of their sustainability disclosures.
